Lymphedema is a progressive, disfiguring, and disabling disease of the skin, classified as a functional, immune, and lymphatic circulatory system disorder (Organic Lymphatic Vascular Disease). The lymphatics are an active and integrated component of the immune response, and in lymphedema, there is always an increased susceptibility to infection due to the compromised immune system. Read about what is an Organic Impairment HERE.
Lymphedema arises when there is a disruption of lymphatic flow (Organic Impairment), leading to the buildup of lymphatic fluid. It is clear that no patient or their lymphedema is the same and neither is its progress. Some patients with lymphedema have few symptoms, and can easily do different degrees of physical activity, while others feel the strain, experience increased swelling with minimum effort, or even suffer varying degrees of disability and severe complications. Read about lymphedema and Infectious Cellulitis HERE.
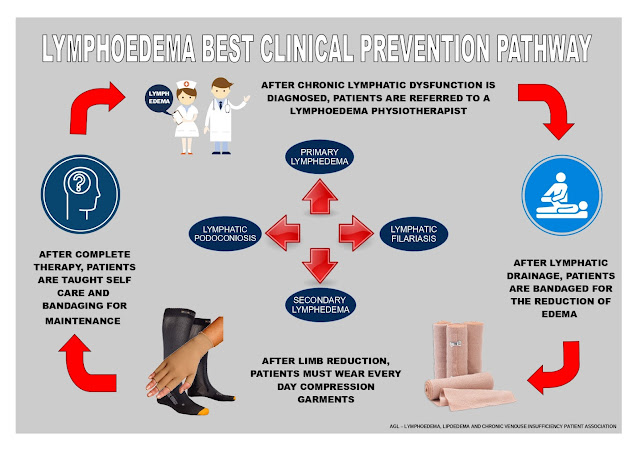
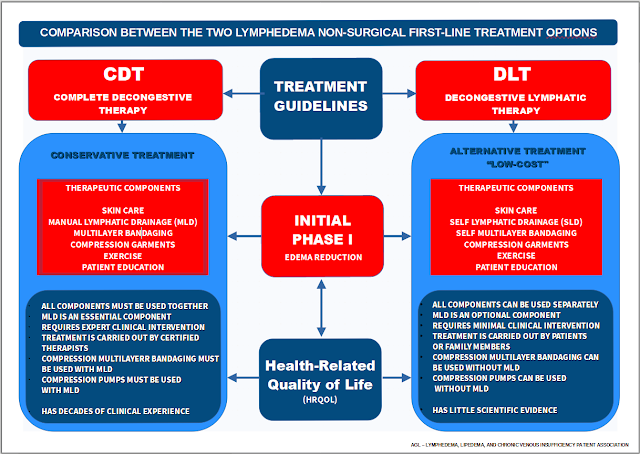
Therapy of peripheral lymphedema is divided into conservative non-operative and operative methods. The best first-line non-surgical treatment for lymphoedema, considered the "Gold Standard" treatment, is known as "COMPLETE DECONGESTIVE THERAPY (CDT)".
Complete Decongestive Therapy is undertaken by a therapist who has undergone training at the specialist level and who combines the following components:
- Skin Care
- Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD)
- Multilayer Bandages
- Exercise
- Compression Garments
- Patient Education
- Compression Pumps (this is an optional adjuvant, and must be accompanied by Manual Lymph Drainage (MLD) conducted by therapists at the specialist level)).
After the initial treatment (Phase 1), which includes all the components and is applied daily and lasts several weeks, the next step is the maintenance treatment (Phase 2), which consists of compression by low-stretch garments, skin care, continued exercise, and MLD as needed. In this second phase, which is long-term, the patient is taught self-bandaging for maintenance, basic self-care of the skin, and exercise practice. Read about which country has the best public healthcare coverage of lymphedema HERE.
The success of Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT) depends on it being administered by an experienced certified therapist. CDT is considered safe, however, patients should consult with their physician before beginning treatment. Indications, contraindications, and the application of individual therapeutic measures depend on several factors: the stage of lymphoedema at the start of treatment, comorbidities, the age of the patient, and the patient’s individual life circumstances.
Failure of Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT) should be confirmed only when intensive non-operative treatment in a clinic specializing in the management of peripheral lymphedema and directed by an experienced clinical lymphologist has been unsuccessful. Read more about the signs, symptoms, and complications of lymphoedema HERE.
In no way should this highly specialized treatment be replaced, due to the possible serious side effects, by edema reduction treatments carried out by non-specialists. Aggressive reduction of swelling can cause skin and vessel damage, Isolated compression therapy of the extremities, particularly in patients with lymphedema also affecting the quadrants of the trunk, may cause displacement of edema and increase swelling at the root of the extremity, and may even lead to genital lymphoedema.
IMPORTANT NOTICE
Lymphedema (Organic Lymphatic Vascular Disease) is due to impaired lymphatic drainage resulting in skin disease, characterized by persistent swelling, and abnormal thickening of the skin and subcutaneous connective tissue. Lymphedema is not just a localized swelling problem, but a condition that can affect multiple body systems, structures and functions, leading to a range of physical, physiological and psychosocial symptoms and complications. Read about the symptoms and complications of lymphedema HERE.
Lymphedema is a serious chronic and progressive disease due to lymphatic dysfunction. The clinical treatment of lymphedema is neither a cosmetic nor an aesthetic treatment. The treatment of lymphedema is to control its progression and alleviate the symptoms related to dysfunction of the lymphatic circulatory system.
To prevent and avoid serious complications associated with treatment, such as the possible displacement of edema to previously unaffected areas when compression therapy is applied for volume reduction, patients should use highly specialized and experienced therapists.
Professional qualification and instruction delivered remotely online are not the same as live hands-on practical instruction in the clinical training and certification of lymphedema therapists, similar to all other rehabilitation, medical, and surgical training programs, and especially for developing the necessary manual skills to treat a disease as complex as lymphedema.
Patients should also take special care when choosing a Multidisciplinary Expert Center of Reference for Lymphedema, as not all countries and centers provide the same treatment options. The best choice is a center of reference that provides Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT”, which is recognized as the Gold Standard treatment for lymphedema.
- Read about what are the principal functions of Manual Lymphatic Drainage HERE.
- Read about what are the main differences between the two principal lymphedema treatment protocols HERE.
- Read about what are the strategies for the implementation of low-cost treatment options for Lymphedema HERE.
REFERENCES
(Click on the texts to read the research articles)
SCIENTIFIC SOCIETIES
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
- lymphedema.
- Biology of Lymphedema
- Lymph vessels: the forgotten second circulation in health and disease
- Lymphatic Vessel Network Structure and Physiology
- Lymphatic System Flows
- Organ-specific lymphatic vasculature: From development to pathophysiology.
- The lymphatic vascular system: much more than just a sewer.
- The unresolved pathophysiology of lymphedema.
- Lymphedema: A Practical Approach and Clinical Update.
- Coagulation in Lymphatic System.
- Regulation of immune function by the lymphatic system in lymphedema.
- Oxidative stress in chronic lymphoedema.
- Regulatory T Cells Mediate Local Immunosuppression in Lymphedema.
- Hemostatic properties of the lymph: relationships with occlusion and thrombosis.
- Secondary lymphedema: Pathogenesis
- Gastrointestinal Lymphatics in Health and Disease
- Intestinal lymphangiectasia in adults
- Role of the lymphatic vasculature in cardiovascular medicine
- The lymphatic vasculature in disease
- Lymphoscintigraphic abnormalities in the contralateral lower limbs of patients with unilateral lymphedema.
- The Prevalence of Lower Limb and Genital Lymphedema after Prostate Cancer Treatment: A Systematic Review
- Peripheral Edema
- The lymphatic system and the skin. Classification, clinical aspects, and histology.
- Lymphedema and cutaneous diseases.
- Lymphedema and subclinical lymphostasis (microlymphedema) facilitate cutaneous infection, inflammatory dermatoses, and neoplasia: A locus minoris resistentiae.
- Serum Immune Proteins in Limb Lymphedema Reflecting Tissue Processes Caused by Lymph Stasis and Chronic Dermato-lymphangio-adenitis (Cellulitis).
- Lymphedema and subclinical lymphostasis (microlymphedema) facilitate cutaneous infection, inflammatory dermatoses, and neoplasia: A locus minoris resistentiae.
- Lymphatic Flow: A Potential Target in Sepsis.
- Infectious complications of lymphedema.
- Acute inflammatory exacerbations in lymphoedema.
- Inflammatory Manifestations of lymphedema.
- Cellulitis.
- Clinical features, microbiological epidemiology, and recommendations for the management of cellulitis in extremity lymphedema.
- Challenges of cellulitis in a lymphedematous extremity.
- Diagnosis and management of cellulitis.
- Cellulitis risk factors for patients with primary or secondary lymphedema.
- Oedema as a risk factor for multiple episodes of cellulitis/erysipelas of the lower leg.
- Prevention of dermatolymphangioadenitis by combined physiotherapy.
- Erysipelas: a common potentially dangerous infection.
- Malignant tumors as complications of lymphedema.
- Lymphedematous areas: Privileged sites for tumors, infections, and immune disorders.
- Lymphedema-related angiogenic tumors and other malignancies.
- Lymphedema: an immunologically vulnerable site for the development of neoplasms.
- Lymph stasis promotes tumor growth
- A retrospective analysis of Stewart-Treves syndrome in the context of chronic lymphedema.
- Stewart-Treves Syndrome
- Congenital lymphedema complicated by pain and psychological distress: case report
- Lymphatic Pain in Breast Cancer Survivors
- Does Manual Lymphatic Drainage Have Any Effect on Pain Threshold and Tolerance of Different Body Parts?
- Lymphedema therapy reduces the volume of edema and pain in patients with breast cancer
- Quality of life in patients with primary and secondary lymphedema in the community
TREATMENT
- Treatment of limbs lymphedema.
- Nonoperative treatment of lymphedema.
- Lymphedema: From diagnosis to treatment.
- Lymphedema-clinical picture and therapy.
- Physiotherapeutic rehabilitation of lymphedema: state-of-the-art.
- Diagnosis and management of lymphatic vascular disease
- Effective treatment of lymphedema of the extremities.
- Lymphoscintigraphic aspects of the effects of manual lymphatic drainage.
- Intensive Treatment of Lower-Limb Lymphedema and Variations in Volume.
- Effectiveness and safety of Complete Decongestive Therapy of Phase I.
- Therapeutic Efficacy of Complex Decongestive Therapy in the Treatment of Elephantiasis of the Lower Extremities.
- Effects of Phase I complex decongestive physiotherapy on physical functions and depression levels in breast cancer-related lymph edema.
- Does lymphoedema bandaging reduce the risk of toe ulceration?
- Study of 700 referrals to a Lymphedema Program.
- Worldwide assessment of healthcare personnel dealing with lymphoedema.
- Földi M, Földi E. Földi’s textbook of lymphology for physicians and Lymphoedema therapists.
- Fluid Shifts Induced by Physical Therapy in Lower Limb Lymphedema Patients
- Visualization of Accessory Lymphatic Pathways, before and after Manual Drainage, in Secondary Upper Limb Lymphedema Using Indocyanine Green Lymphography
- The risk of genital edema after external pump compression for lower limb lymphedema.
- The management of genital lymphoedema
- The management of deep vein thrombosis in lymphoedema: a review.
- Lymphedema-associated comorbidities and treatment gap.
- A study of the advantages of elastic stockings for leg lymphedema.
- Indications for medical compression stockings in venous and lymphatic disorders: An evidence-based consensus statement.
- Medical compression stockings for chronic venous diseases and lymphedema: Scientific evidence and results of a patient survey on quality of care.
- Impact of Compression Therapy on Cellulitis (ICTOC) in adults with chronic edema: a randomized controlled trial protocol.
- Compression Therapy Is Cost-Saving in the Prevention of Lower Limb Recurrent Cellulitis in Patients with Chronic Edema.
- Occupational leg edema-use of compression stockings.
DISABILITY
- Disability and lymphedema.
- Lymphedema and employability.
- Worse and worse off: the impact of lymphedema on work and career after breast cancer
- Functioning in lymphedema from the patient's perspective using the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF).
- Unilateral upper extremity lymphedema deteriorates the postural stability in breast cancer survivors
- Postural Stability in Patients with Lower Limb Lymphedema
- Disability, psychological distress and quality of life in breast cancer survivors with arm lymphedema
DISFIGUREMENT
- Adjusting to disfigurement: processes involved in dealing with being visibly different
- Quality of Life in Cancer Patients with Disfigurement due to Cancer and its Treatments
- Quality-of-life and body image impairments in patients with lymphedema
- Association of lower extremity lymphedema with pelvic floor functions, sleep quality, kinesiophobia, body image in patients with gynecological cancers
QUALITY OF LIFE
- The impact of lower limb chronic oedema on patients' quality of life
- Quality of life in patients with primary and secondary lymphedema in the community
- Evaluating the effect of upper-body morbidity on quality of life following breast cancer treatment.
- Functionality and quality of life of patients with unilateral lymphedema of a lower limb: a cross-sectional study
- The effect of complete decongestive therapy on the quality of life of patients with peripheral lymphedema
PSYCHOSOCIAL IMPACT
- Psychosocial Impact of Lymphedema.
- Associations between chronic disease, age and physical and mental health status
- A network analysis of psychological flexibility, coping, and stigma in dermatology patients
- 'Abandoned by medicine'? A qualitative study of women's experiences with lymphoedema secondary to cancer, and the implications for care
- People are neglected, not diseases.
- Chronic edema/lymphoedema: under-recognized and under‐treated.
- Lymphatic Medicine: Paradoxically and unnecessarily ignored.
- Medical education: a deficiency or a disgrace.
PEDIATRIC LYMPHEDEMA
- NORD: Rare Disease Database - Lymphedema
- Medical management of lymphedema.
- Primary lymphedema in childhood.
- An approach to familiar lymphedema
- Pediatric Children Lymphedema
- Primary Lymphedema French National Diagnosis and Care Protocol (PNDS).
- Lymphatic filariasis: an infection of childhood.
- Lymphatic filariasis in children: clinical features, infection burdens and future prospects for elimination.
- Podoconiosis: Clinical spectrum and microscopic presentations.
- Podoconiosis: A Possible Cause of Lymphedema in Micronesia.
- A cross-sectional study to evaluate depression and quality of life among patients with lymphoedema due to podoconiosis, lymphatic filariasis, and leprosy.
- The impact of acute adenolymphangitis in podoconiosis on caregivers.
- Neglected tropical diseases and disability-what is the link?
- Locomotor disability in bancroftian filarial lymphoedema patients.
- Neglected patients with a neglected disease?
- Neglected tropical diseases and mental health: a perspective on comorbidity.
- People are neglected, not diseases.
- Addressing Inequity: Neglected Tropical Diseases and Human Rights.
- Neglected Tropical Diseases, Conflict, and the Right To Health.
- Peripheral Edema
- Phlebolymphedema
- Understanding Chronic Venous Disease: A Critical Overview of Its Pathophysiology and Medical Management
- Role of the lymphatic vasculature in cardiovascular medicine
- Communication between lymphatic and venous systems
- Phlebopathies and occupation
- Phlebopathies and workers
- Evidence of health risks associated with prolonged standing at work and intervention effectiveness
- Leg edema formation and venous blood flow velocity during a simulated long-haul flight